Blog
Hyper Pigmentation Treatment Options
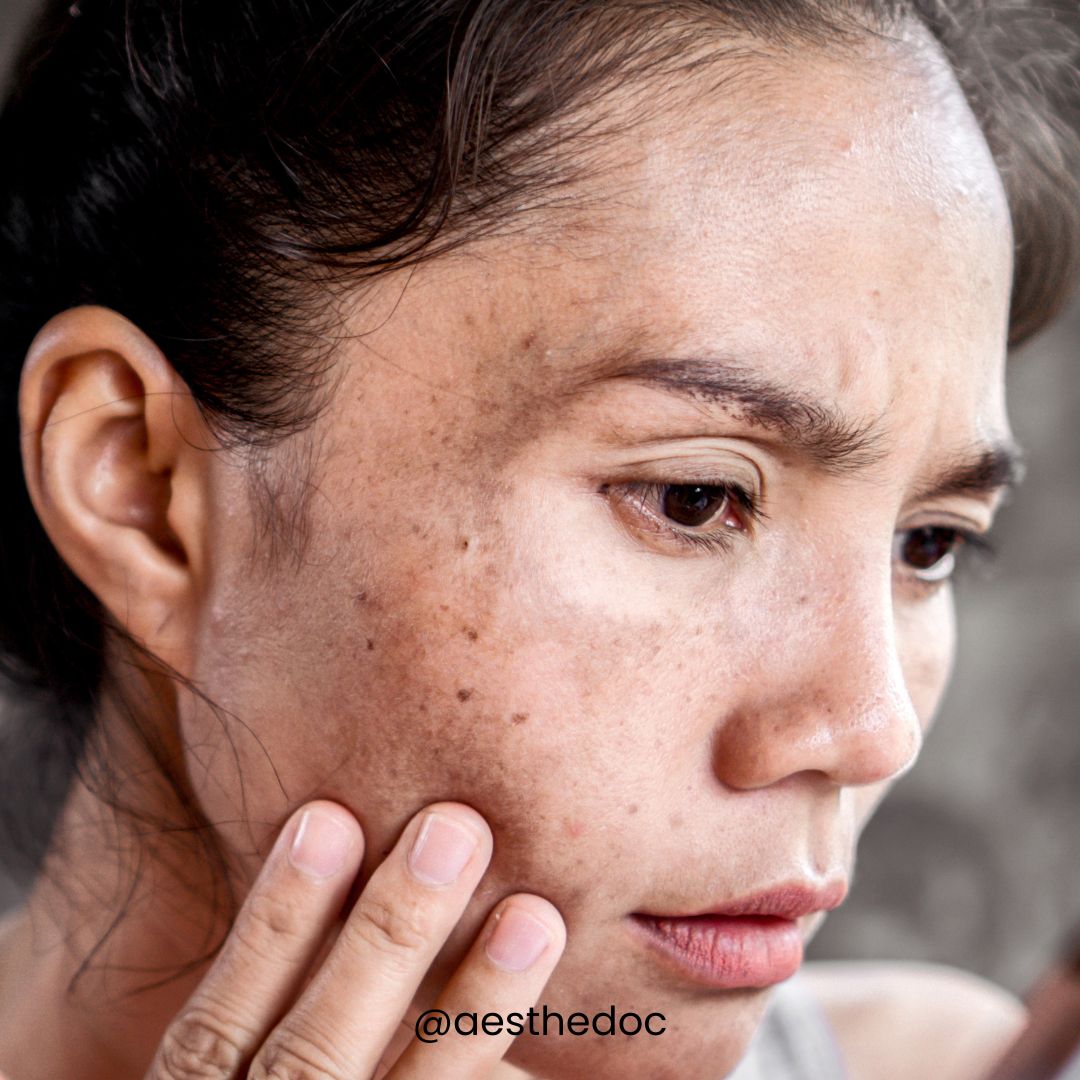

What is Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation refers to the natural color of a person’s skin, determined by the amount and type of melanin—a pigment produced by melanocyte cells. Melanin production is influenced by sun exposure, genetics, hormonal changes, and environmental factors. It protects the skin from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
What Causes Excessive Skin Pigmentation?
Excessive skin pigmentation, or hyperpigmentation, can be caused by several factors, including:
- Sun Exposure: UV radiation triggers the skin to produce excess melanin, leading to dark spots or patches.
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, menopause, or hormonal medications can cause hyperpigmentation.
- Inflammation or Injury: Conditions like acne, eczema, psoriasis, or injuries can increase melanin production, resulting in hyperpigmentation.
- Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to hyperpigmentation.
- Aging: The skin’s natural ability to produce melanin may increase with age, leading to dark spots.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics, anti-seizure drugs, and chemotherapy, can cause hyperpigmentation as a side effect.
In some cases, excessive skin pigmentation may be a symptom of medical conditions like Addison’s disease, Cushing’s syndrome, or hemochromatosis. Consult a healthcare professional if you have concerns.
Types of Skin Pigmentation
Pigmentation refers to the coloring of skin, hair, or eyes caused by melanocyte cells. It can occur naturally or due to various factors like genetics, sun exposure, hormonal changes, or medical conditions.
Here are some common types of pigmentation:
- Melasma: Characterized by dark, irregular patches, melasma often occurs in women due to hormonal changes like pregnancy or contraceptive use. Sun exposure can worsen it.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): This occurs when the skin produces excess melanin in response to inflammation or injury, often following acne, bug bites, or skin trauma.
- Sunspots: Also known as solar lentigines or age spots, these small, flat, brown or black spots are caused by sun exposure and commonly appear on the face, hands, and arms, especially in people over 50.
- Freckles: These small, flat brown spots are usually caused by sun exposure and are most common in people with fair skin and red or blonde hair.
- Albinism: A rare genetic condition where melanin production is minimal or absent, leading to very light skin, hair, and eyes, often accompanied by vision problems.
- Vitiligo: A condition where the skin loses its pigment in patches, thought to be an autoimmune disorder that attacks melanocytes.
- Hemangiomas: Red or purple birthmarks caused by abnormal blood vessel growth in the skin, common in infants and typically resolving by age 10.
Melasma, Freckles, and Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
These conditions can develop due to factors like sun exposure, hormonal changes, and skin injuries:
- Melasma is often triggered by hormonal changes during pregnancy or contraceptive use. Sunlight and heat can worsen the condition.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH) often occurs after skin inflammation or injury, such as acne. It can also result from cosmetic procedures like dermabrasion, laser treatments, and chemical peels.
- Freckles are typically caused by UV exposure, with individuals who have fair skin being more prone to developing them.
Steroid-Based Creams for Skin Treatment
Steroid creams reduce inflammation and itching in the skin by decreasing immune system activity. They are commonly used to treat conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and allergic reactions.
Some common over-the-counter (OTC) and prescription-based steroid creams include:
- Hydrocortisone Cream: A mild OTC steroid cream used for temporary relief from mild skin inflammation and itching.
- Triamcinolone Acetonide Cream: A medium-strength steroid cream for treating eczema and psoriasis, available OTC or by prescription.
- Betamethasone Valerate Cream: A stronger steroid cream used for moderate to severe skin conditions like psoriasis.
- Mometasone Furoate Cream: A potent steroid cream for moderate to severe conditions, available by prescription.
Overuse of steroid creams can lead to side effects like skin thinning, stretch marks, and infections, so it’s essential to use them only as directed.
Quick Fixes with Steroid-Based Creams
Steroid creams can offer quick relief from mild skin inflammation, but even low-potency creams should be used cautiously to avoid side effects. For persistent or severe skin conditions, always consult a healthcare provider.
Advanced Skin Pigmentation Treatments at Lemonade Aesthetics
At Lemonade Aesthetics Boutique Clinic in Islamabad, we offer a wide range of advanced treatments for skin pigmentation. Our highly trained professionals use the latest technologies and techniques to provide safe, effective, and long-lasting results.
Book a consultation today and discover how our world-class treatments can help you achieve the healthy, confident skin you deserve.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can I prevent skin pigmentation?
You can prevent skin pigmentation by wearing sunscreen daily, avoiding excessive sun exposure, using gentle skincare products, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
How can I treat skin pigmentation?
Treatment options include topical creams, chemical peels, laser treatments, and microdermabrasion, depending on the type and severity of pigmentation.
Is skin pigmentation dangerous?
In most cases, skin pigmentation is not dangerous, but in some instances, it may signal underlying medical conditions. Consult a dermatologist for unusual changes.
Can skin pigmentation be permanent?
Some pigmentation, like freckles and age spots, may be permanent. Other types, such as melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, may fade with proper treatment.
Blog
Laser Hair Removal Bahria Town Phase 7 Rawalpindi
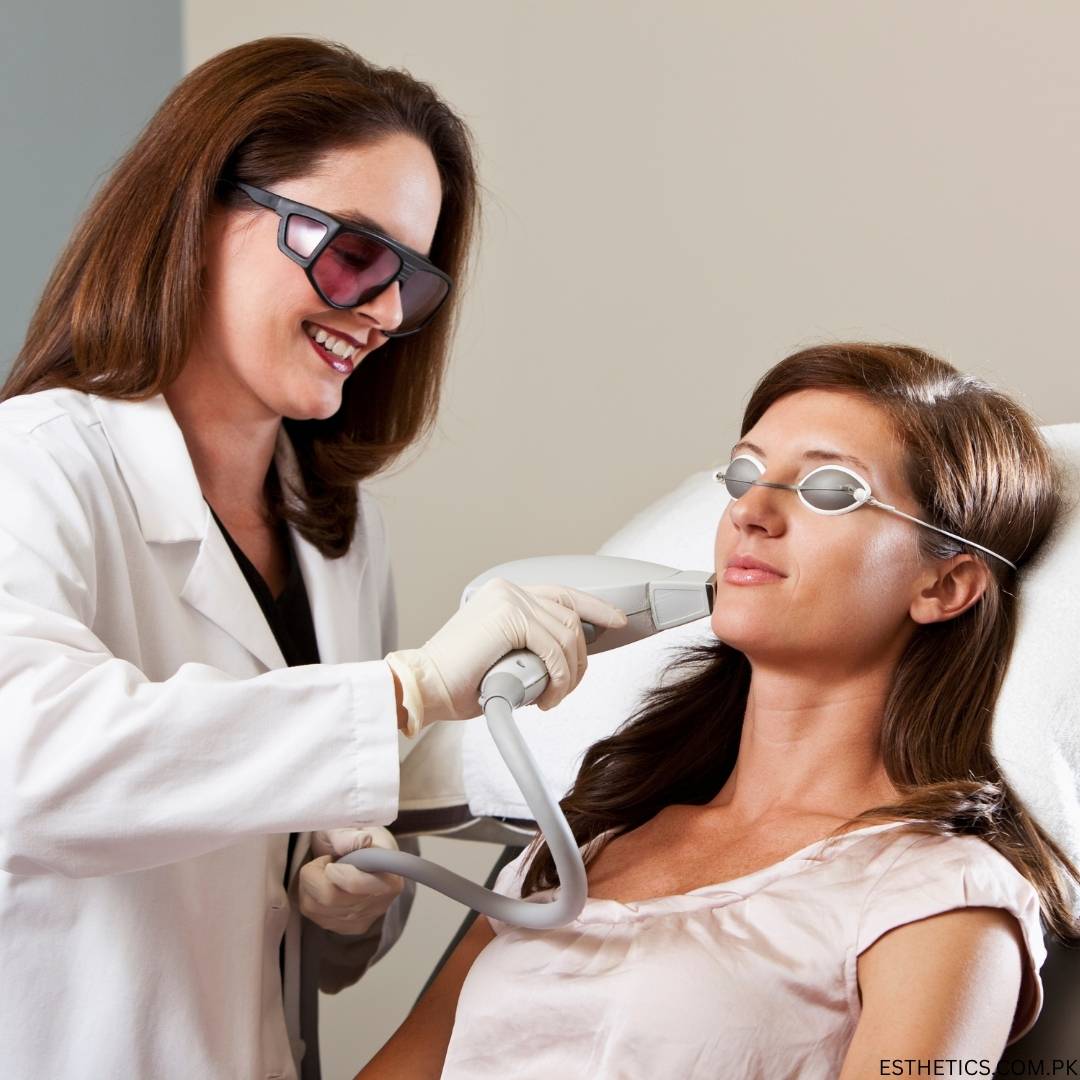
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced lifestyle, many men and women are tired of dealing with unwanted hair through temporary methods such as waxing, shaving, threading, or using depilatory creams. These methods not only take time but also cause side effects like skin irritation, ingrown hairs, and rapid regrowth.
This is where laser hair removal comes as a modern, safe, and long-lasting solution. If you are living in Bahria Town Phase 7 Rawalpindi, you now have access to advanced technology and experienced dermatologists right at your doorstep.
This detailed guide will cover everything you need to know about laser hair removal in Bahria Town Phase 7—from how it works, benefits, and number of sessions required, to the cost estimate for different body areas. By the end, we’ll also guide you to Aesthedoc Clinic, one of the top destinations for safe and effective laser hair removal.
What is Laser Hair Removal?
Laser hair removal is a medical aesthetic procedure that uses highly concentrated light beams to target hair follicles. The pigment (melanin) in the hair absorbs the laser energy, which destroys the follicle and reduces future growth.
It is considered one of the most effective methods for permanent hair reduction. Unlike waxing or shaving, which only remove surface hair, laser treatment targets the root of the problem—the follicle.
How Does It Work?
The procedure is simple and usually involves the following steps:
- Consultation & Skin Analysis – Your skin type and hair texture are assessed by a dermatologist.
- Preparation – The treatment area is shaved before the procedure to allow the laser to penetrate better.
- Laser Application – A handheld device delivers light pulses to the hair follicles. Cooling technology keeps the skin comfortable.
- Post-Treatment Care – Sunscreen and soothing gels are applied. You are advised to avoid sun exposure for a few days.
Why Laser Hair Removal is Popular in Bahria Town Phase 7 Rawalpindi
Bahria Town Phase 7 is one of the most modern and well-developed areas of Rawalpindi, home to a large community that values convenience, advanced lifestyle, and self-care. Residents here prefer treatments that are time-saving, effective, and reliable.
Laser hair removal fits perfectly into this lifestyle because it:
- Reduces salon visits.
- Offers long-term results with minimal maintenance.
- Provides smooth, flawless skin that boosts confidence.
Benefits of Laser Hair Removal
Laser hair removal has multiple advantages over traditional methods. Let’s look at them in detail:
- Permanent Hair Reduction – Up to 90% reduction after multiple sessions.
- No More Waxing Pain – Say goodbye to painful waxing strips and razor burns.
- Safe for All Areas – Can be performed on face, underarms, arms, legs, bikini, back, and chest.
- Quick & Convenient – Small areas like upper lip take just 5 minutes.
- Cost-Effective – Though the upfront cost seems high, it saves money spent on lifelong waxing/shaving.
- No Ingrown Hairs – Prevents bumps and skin irritation caused by other methods.
- Boosted Confidence – Smooth skin helps you feel confident in your everyday and professional life.
Who Can Get Laser Hair Removal?
Laser hair removal is suitable for both men and women. It works best for individuals with:
- Dark, coarse hair and light skin (though modern lasers also work on darker skin tones).
- Unwanted hair on the face, underarms, arms, legs, bikini, chest, or back.
- Busy lifestyles with no time for repeated waxing or shaving.
- Skin prone to ingrown hairs or razor bumps.
❌ However, it is not recommended for:
- Pregnant women.
- People with certain skin disorders or infections.
- Those with very light blonde, grey, or white hair (less melanin = less effectiveness).
How Many Sessions Are Required?
Laser hair removal usually requires 6–8 sessions for the best results.
- Face & small areas: 4–6 sessions.
- Arms & legs: 6–8 sessions.
- Back & chest (men): 8–10 sessions.
Sessions are spaced 4–6 weeks apart, depending on the hair growth cycle.
Side Effects & Safety
When done under professional supervision, laser hair removal is safe and FDA-approved. Some mild side effects may include:
- Redness or slight swelling (subsides in a few hours).
- Temporary skin sensitivity.
These are completely normal and can be managed with aftercare instructions provided by your dermatologist.
Estimated Prices of Laser Hair Removal in Bahria Town Phase 7 Rawalpindi
Prices vary depending on the size of the treatment area, number of sessions, and technology used. Here’s an estimated price range:
| Body Area | Estimated Price Per Session (PKR) | Package (6 Sessions) |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Lip | 2,500 – 3,500 | 12,000 – 15,000 |
| Chin | 3,000 – 4,500 | 15,000 – 18,000 |
| Full Face | 8,000 – 10,000 | 40,000 – 50,000 |
| Underarms | 4,000 – 5,000 | 20,000 – 25,000 |
| Full Arms | 10,000 – 12,000 | 50,000 – 60,000 |
| Full Legs | 15,000 – 18,000 | 75,000 – 90,000 |
| Bikini Line | 7,000 – 9,000 | 35,000 – 45,000 |
| Chest (Men) | 12,000 – 15,000 | 60,000 – 75,000 |
| Back (Men) | 15,000 – 18,000 | 75,000 – 90,000 |
| Full Body (Men/Women) | 35,000 – 45,000 | 180,000 – 220,000 |
💡 Tip: Prices may differ slightly depending on hair thickness and number of sessions required. Always book a consultation for an exact quote.
Preparing for Your Laser Session
To get the best results, follow these preparation steps:
- Avoid waxing, plucking, or threading 4 weeks before treatment.
- Shave the area 24 hours before the session.
- Avoid tanning and direct sunlight.
- Inform your doctor about any medications you are taking.
Aftercare Tips
Post-treatment care is important to protect your skin:
- Apply sunscreen regularly.
- Avoid hot showers or saunas for 24 hours.
- Use soothing creams or aloe vera gel.
- Do not scratch or pick treated areas.
FAQs About Laser Hair Removal in Bahria Town Phase 7 Rawalpindi
Q1: Is laser hair removal painful?
➡ Modern machines with cooling systems make it almost painless, with only a slight tingling sensation.
Q2: How long does each session take?
➡ Small areas like upper lip take 5–10 minutes, while full body can take 1.5–2 hours.
Q3: Can men also get laser hair removal?
➡ Yes, many men opt for chest, back, shoulders, and beard shaping.
Q4: Is laser hair removal permanent?
➡ It offers permanent hair reduction (up to 90%). Some fine regrowth may appear, requiring maintenance once or twice a year.
Q5: Which clinic is best for laser hair removal in Bahria Town Phase 7?
➡ Aesthedoc Clinic is one of the top choices, offering safe and affordable treatments with advanced technology.
Why Choose Aesthedoc Clinic in Bahria Town Phase 7 Rawalpindi?
When it comes to your skin, you deserve nothing but the best. Aesthedoc Clinic offers:
- 🩺 Experienced dermatologists & certified technicians.
- FDA-approved machines with cooling technology.
- Personalized treatment plans.
- A hygienic, comfortable, and professional environment.
- Affordable packages for multiple areas.
Whether you want to treat a small area or go for full-body laser, Aesthedoc ensures safe, effective, and long-lasting results.
Final Thoughts
If you are searching for laser hair removal in Bahria Town Phase 7 Rawalpindi, you now have a reliable, safe, and effective solution available locally. No more painful waxing or endless shaving—laser treatment gives you smooth, confident, and hair-free skin.
👉 Book your consultation at Aesthedoc Clinic today and take the first step toward a lifetime of convenience and confidence.
📍 Location: Bahria Town Phase 7 Rawalpindi
📞 Contact: Aesthedoc Clinic
Blog
Laser Hair Removal in Bahria Town Phase 8 Rawalpindi
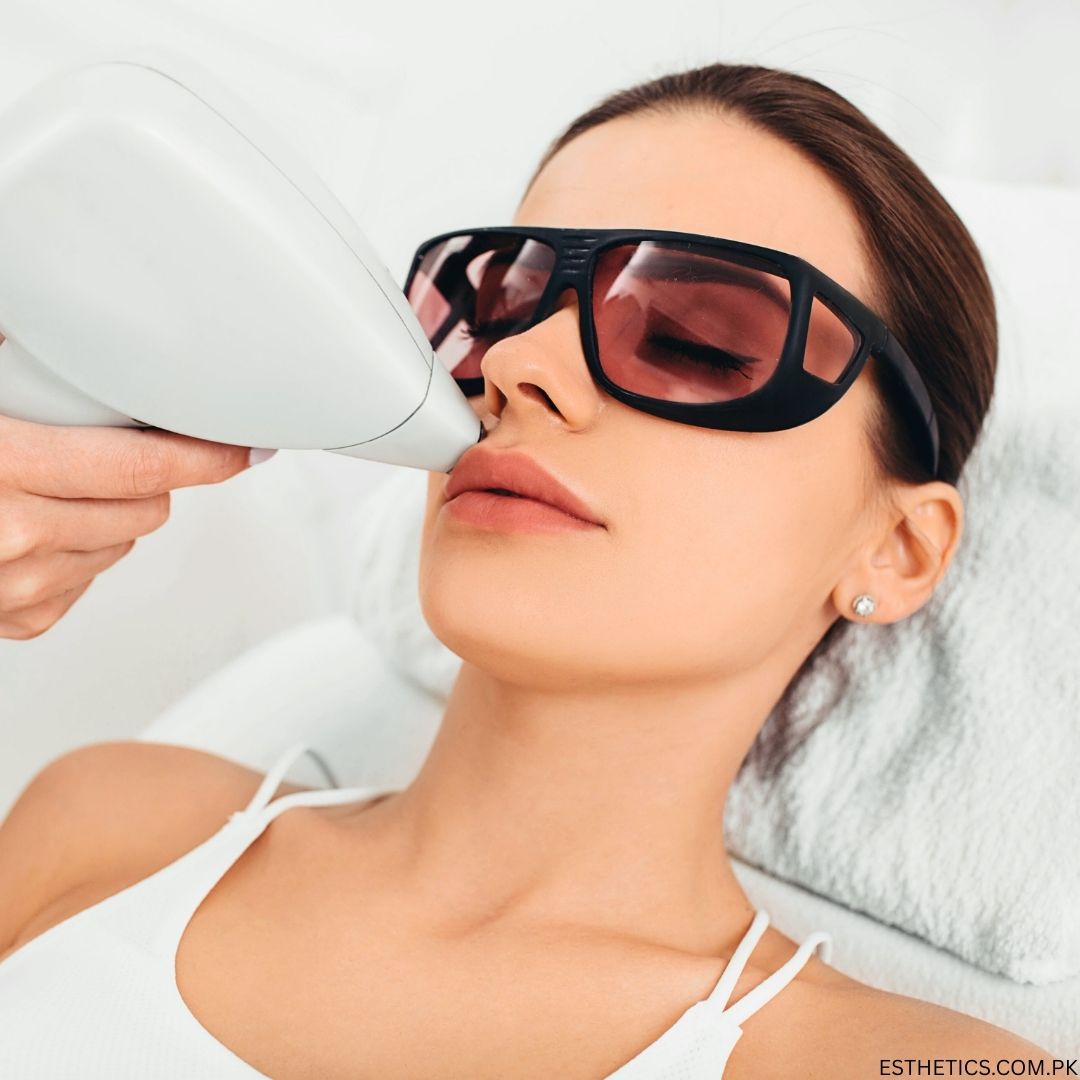

Introduction
Unwanted body hair is one of the most common concerns for both men and women. Shaving, waxing, or threading can be time-consuming, painful, and temporary. This is why laser hair removal has become the most trusted and long-lasting solution for smooth, hair-free skin.
If you live in Bahria Town Phase 8 Rawalpindi, you no longer need to travel far to get world-class laser treatments. With advanced machines, expert dermatologists, and affordable packages, laser hair removal is now available right in your neighborhood.
In this guide, we’ll explore the benefits, procedure, estimated prices for different body areas, and why Aesthedoc Clinic in Bahria Town Phase 8 Rawalpindi is the right choice for your treatment.
What is Laser Hair Removal?
Laser hair removal is a medical procedure that uses concentrated light beams to target and destroy hair follicles. The pigment (melanin) in the hair absorbs the light, which damages the follicle and prevents future growth.
It’s a safe, FDA-approved, and effective treatment that reduces up to 90% of hair permanently after multiple sessions.
Benefits of Laser Hair Removal in Bahria Town Phase 8 Rawalpindi
Choosing laser over traditional methods has countless advantages:
- ✅ Long-Lasting Results – Smooth skin for months and years with maintenance sessions.
- ✅ Cost-Effective – No need to spend money repeatedly on waxing or razors.
- ✅ Quick Sessions – Small areas take just a few minutes.
- ✅ Safe & Painless – Modern machines offer cooling technology for a comfortable experience.
- ✅ No Ingrown Hairs – Unlike waxing or shaving, laser prevents irritation and bumps.
Laser Hair Removal Prices in Bahria Town Phase 8 Rawalpindi
The cost of laser hair removal depends on the size of the treatment area, number of sessions, and the clinic’s expertise. Below is an estimated price table for popular treatment areas in Bahria Town Phase 8 Rawalpindi:
| Body Area | Estimated Price Per Session (PKR) | Package (6 Sessions) |
|---|---|---|
| Upper Lip | 2,500 – 3,500 | 12,000 – 15,000 |
| Chin | 3,000 – 4,000 | 15,000 – 18,000 |
| Full Face | 8,000 – 10,000 | 40,000 – 50,000 |
| Underarms | 4,000 – 5,000 | 20,000 – 25,000 |
| Full Arms | 10,000 – 12,000 | 50,000 – 60,000 |
| Full Legs | 15,000 – 18,000 | 75,000 – 90,000 |
| Bikini Line | 7,000 – 9,000 | 35,000 – 45,000 |
| Chest (Men) | 12,000 – 15,000 | 60,000 – 75,000 |
| Back (Men) | 15,000 – 18,000 | 75,000 – 90,000 |
| Full Body (Men/Women) | 35,000 – 45,000 | 180,000 – 220,000 |
💡 Note: Prices may vary depending on hair type, skin tone, and machine technology used. A consultation with a dermatologist at Aesthedoc Clinic will provide exact cost details.
How Many Sessions Are Required?
Most clients require 6 to 8 sessions spaced 4 to 6 weeks apart for optimal results. Maintenance sessions may be needed once or twice a year to keep skin permanently smooth.
Why Choose Aesthedoc Clinic in Bahria Town Phase 8 Rawalpindi?
If you are searching for the best clinic for laser hair removal in Bahria Town Phase 8 Rawalpindi, Aesthedoc Clinic stands out for several reasons:
- Experienced Dermatologists & Aesthetic Physicians
- FDA-Approved Laser Machines with Cooling Technology
- Personalized Treatment Plans for each skin and hair type
- Hygienic & Comfortable Environment
- Affordable Packages & Discounts for multiple areas
With its professional team and modern technology, Aesthedoc Clinic ensures safe, effective, and lasting results for men and women.
Final Thoughts
Laser hair removal is more than a cosmetic treatment – it’s an investment in your confidence, comfort, and long-term savings. If you’re tired of waxing or shaving, it’s time to switch to the most reliable solution.
For laser hair removal in Bahria Town Phase 8 Rawalpindi, book your consultation at Aesthedoc Clinic today and take the first step toward smooth, hair-free skin.
📍 Visit us in Bahria Town Phase 8 Rawalpindi
📞 Contact Aesthedoc Clinic to schedule your appointment
Blog
Aesthetic Machines Supplier Pakistan
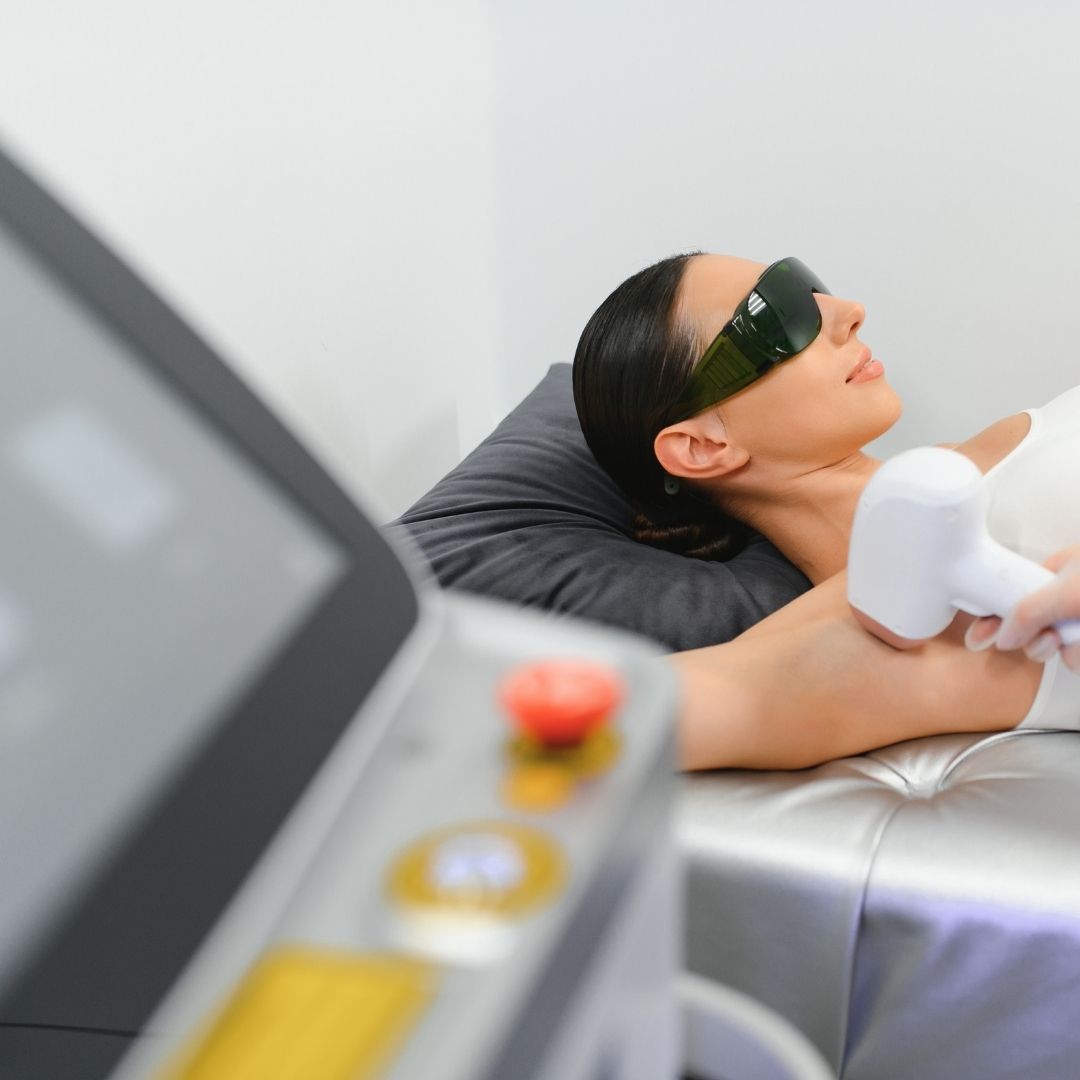
Introduction
In Pakistan, the field of aesthetic medicine has grown tremendously over the past decade. Patients are no longer seeking only injectables like Botox and fillers but are increasingly demanding non-invasive and minimally invasive machine-based treatments. From laser hair removal and HIFU facelifts to HydraFacial treatments, body contouring, CO₂ fractional lasers, and RF microneedling, the use of advanced aesthetic machines is now a cornerstone of modern dermatology and cosmetic practices.
For clinics, medspas, and dermatologists, the challenge is to find an authentic and trusted aesthetic machines supplier in Pakistan who can provide safe, FDA-approved, and clinically reliable systems. This is where Aesthedoc steps in as the most reliable partner.
At Aesthedoc Shop, you can buy a wide range of aesthetic devices and equipment including:
- Laser Hair Removal Machines
- HIFU Skin Tightening Machines
- HydraFacial & Aqua Peeling Systems
- CO₂ Fractional Lasers
- RF Microneedling Devices
- Cryolipolysis Fat Freezing Machines
- Body Contouring & EMSculpt Devices
- PRP Centrifuge Machines
- Skin Analysis & Diagnostic Systems
This article will give you a detailed overview of all the major aesthetic machines available in Pakistan, their uses, and why Aesthedoc should be your go-to supplier.
Why Choose Authentic Aesthetic Machines in Pakistan?
The aesthetic industry in Pakistan is highly competitive, and with growing patient awareness, clinics cannot compromise on the quality of their devices. Using low-quality or counterfeit machines poses serious risks:
- Unsafe procedures leading to burns, scarring, or treatment failure.
- Short device lifespan due to poor build quality.
- No warranty or after-sales service.
- Legal and reputational risks for clinics.
On the other hand, authentic and FDA/CE-certified devices provide:
- Consistent treatment results.
- Patient safety and satisfaction.
- Long-term ROI (Return on Investment) for clinics.
- Brand credibility.
Aesthedoc guarantees authentic machines sourced from verified manufacturers with proper handling, installation, and nationwide delivery.
Categories of Aesthetic Machines in Pakistan
Let’s explore the most in-demand aesthetic machines available in Pakistan and supplied by Aesthedoc.
1. Laser Hair Removal Machines in Pakistan
Laser hair removal is one of the most sought-after aesthetic procedures in Pakistan. A good laser hair removal machine supplier must provide systems that are safe for all skin types, especially South Asian tones.
Types of Laser Hair Removal Machines Available:
- Diode Laser (most popular in Pakistan)
- Alexandrite Laser (effective for lighter skin)
- Nd:YAG Laser (safe for darker tones)
Top Global Brands Used in Pakistan:
- Alma Soprano ICE / Titanium
- Candela GentleLase & GentleYAG
- Cynosure Elite+
- Lumenis LightSheer
Applications:
- Permanent hair reduction
- Suitable for face, arms, legs, underarms, bikini, and full body
👉 Buy authentic laser hair removal machines in Pakistan from Aesthedoc Shop.
2. HIFU (High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound) Machines in Pakistan
HIFU is one of the most effective non-surgical facelift technologies available today. It uses ultrasound energy to target deep skin layers, stimulating collagen and providing a natural lift.
Uses of HIFU Machines:
- Non-surgical facelift
- Jawline tightening
- Wrinkle reduction
- Neck and décolleté rejuvenation
Popular HIFU Systems:
- Ultraformer III
- Doublo Gold
- Ultraformer MPT
These machines are highly in demand in Islamabad, Lahore, Karachi, and Rawalpindi clinics.
3. HydraFacial & Aqua Peeling Machines in Pakistan
HydraFacial treatments are extremely popular among Pakistani clients for skin cleansing, hydration, and glow.
Benefits of HydraFacial Machines:
- Deep cleansing and exfoliation
- Blackhead and oil removal
- Hydration with serums
- Improved skin tone and texture
Popular Systems in Pakistan:
- Original HydraFacial MD®
- AquaSure H2
- Korean Aqua Peeling Devices
These machines are a must-have for dermatology clinics and beauty spas.
4. CO₂ Fractional Lasers in Pakistan
CO₂ lasers are considered the gold standard for skin resurfacing and scar treatment.
Applications of CO₂ Fractional Lasers:
- Acne scar treatment
- Wrinkle reduction
- Skin resurfacing and tightening
- Stretch mark reduction
Top CO₂ Laser Brands:
- Lutronic eCO2
- DEKA SmartXide
- Lumenis Ultrapulse
Clinics across Pakistan are using these devices for deep skin rejuvenation.
5. RF Microneedling Machines in Pakistan
Radiofrequency (RF) microneedling combines collagen induction therapy with energy-based tightening.
Benefits:
- Acne scar reduction
- Pore size minimization
- Skin tightening
- Stretch mark treatment
Popular RF Microneedling Devices:
- Morpheus8 (by InMode)
- Scarlet RF
- Secret RF
These devices are considered game-changers for acne scar and skin rejuvenation treatments.
6. Cryolipolysis / Fat Freezing Machines in Pakistan
Cryolipolysis, commonly known as fat freezing, is a non-invasive alternative to liposuction.
Uses of Cryolipolysis Machines:
- Double chin fat reduction
- Abdominal fat removal
- Thigh and arm contouring
Popular Devices:
- CoolSculpting® by Allergan
- Clatuu Alpha
- Ice-Shaping Fat Freezers
👉 Many weight loss clinics in Pakistan are investing in these devices.
7. Body Contouring & EMSculpt Devices in Pakistan
These devices combine high-intensity focused electromagnetic energy (HIFEM) to build muscle while reducing fat.
Applications:
- Muscle toning (abs, buttocks, arms)
- Fat burning
- Post-pregnancy body shaping
Popular Brands:
- EMSculpt Neo®
- TeslaFormer®
Clinics in Pakistan are increasingly offering non-surgical body shaping treatments with these machines.
8. PRP Centrifuge Machines in Pakistan
PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma) therapy is widely used for hair restoration, skin rejuvenation, and healing.
PRP Machines Available:
- Laboratory-grade centrifuge machines
- PRP kits for clinical use
They are essential for dermatologists offering PRP for hair loss and facial rejuvenation.
9. Skin Analysis & Diagnostic Systems
A professional skin analysis machine helps clinics:
- Diagnose skin conditions
- Plan treatments
- Track progress
Popular Devices:
- OBSERV 520x
- VISIA Skin Analysis
These systems are highly recommended for modern aesthetic clinics in Pakistan.
Why Buy Aesthetic Machines from Aesthedoc?
When searching for the best aesthetic machines supplier in Pakistan, here’s why Aesthedoc stands out:
- Authentic, original machines only (no fakes or cheap replicas)
- Wide range of devices (lasers, HIFU, HydraFacial, body contouring)
- Competitive pricing tailored for Pakistan’s market
- Proper warranty and after-sales support
- Nationwide delivery with safe installation
- Easy online purchase
Conclusion
The aesthetic industry in Pakistan is expanding rapidly, and patients are demanding non-surgical, advanced, and machine-based treatments. For clinics and practitioners, investing in authentic machines is not just about technology – it is about patient safety, credibility, and long-term success.
Whether you are looking for laser hair removal machines, HIFU devices, HydraFacial systems, CO₂ lasers, body contouring machines, RF microneedling, cryolipolysis, or PRP equipment, the most trusted partner is Aesthedoc.
👉 Visit Aesthedoc today to explore and order authentic aesthetic machines in Pakistan.
-

 Aesthetics Medicine2 years ago
Aesthetics Medicine2 years agoFat Dissolving Injections
-

 Aesthetics Medicine2 years ago
Aesthetics Medicine2 years agoAesthetic Medicine Supplier Pakistan
-
 Aesthetics2 years ago
Aesthetics2 years agoFace Thread Lift
-

 Aesthetics2 years ago
Aesthetics2 years agoEnlargement Male Breast Tissues in Blue Area, Gynecomastia Self-Care
-

 Aesthetics2 years ago
Aesthetics2 years agoFat Dissolving Injections Price in Pakistan
-

 Blog3 years ago
Blog3 years agoTop 5 Fat Dissolving Injections
-

 Blog3 years ago
Blog3 years agoFat Loss Injections Benefits Risk Side Effects
-

 Blog3 years ago
Blog3 years agoFat Dissolving Injections Reality Truth and Fact?


